Artificial Carbon Sequestration Plants

















SUNY Binghamton's Plant Helps Sustainable Carbon Capture
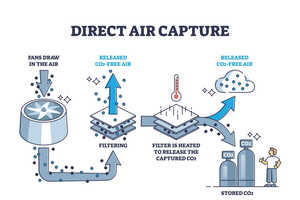
Georgia Wray Norsten — February 4, 2025The Artificial Carbon Sequestration Plant developed by SUNY Binghamton is a significant step toward sustainable carbon capture and clean energy generation. Designed with bacteria-based solar cells, the plant mimics natural processes but captures carbon dioxide 10 times more efficiently while also generating electricity. This innovation presents a promising solution for reducing indoor carbon levels and mitigating climate change.
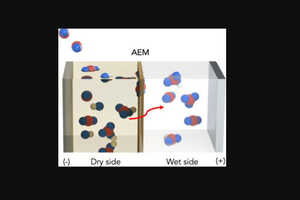
Unlike traditional carbon capture technologies, this artificial plant features cyanobacteria-powered biological solar cells that photosynthesize efficiently, reducing indoor CO₂ levels by 90% -- far outperforming natural plants. The captured energy can also power small electronic devices, making it a dual-purpose sustainability breakthrough.
The project underscores the growing potential of engineered nature-based solutions in environmental conservation and energy innovation. As researchers continue refining the technology, this artificial plant could become an integral tool for carbon-neutral buildings, cleaner indoor air, and renewable energy production, reinforcing the role of science in tackling climate challenges.



